What if you could buy a Yamaha synth with AWM2, AN and VL synthesis and buy it today? It’s not the unicorn super-Montage, it’s the Yamaha EX5 (released in 1998). The EX5 supports:
- AWM tone generation
- VL tone generation
- AN tone generation, and
- FDSP tone generation.
The EX5 had brothers, the EX5R rack module, and the diminuitive EX7. The EX7 is more limited in a number of ways including the absence of VL. Formulated Digital Sound Processing (FDSP) is a note- and velocity-dependent effect processor — an early version of Virtual Circuit Modeling. FDSP models electromagnetic pick-ups, water, PWM, flanger, phaser, etc. [I won’t say too much more about FDSP.]
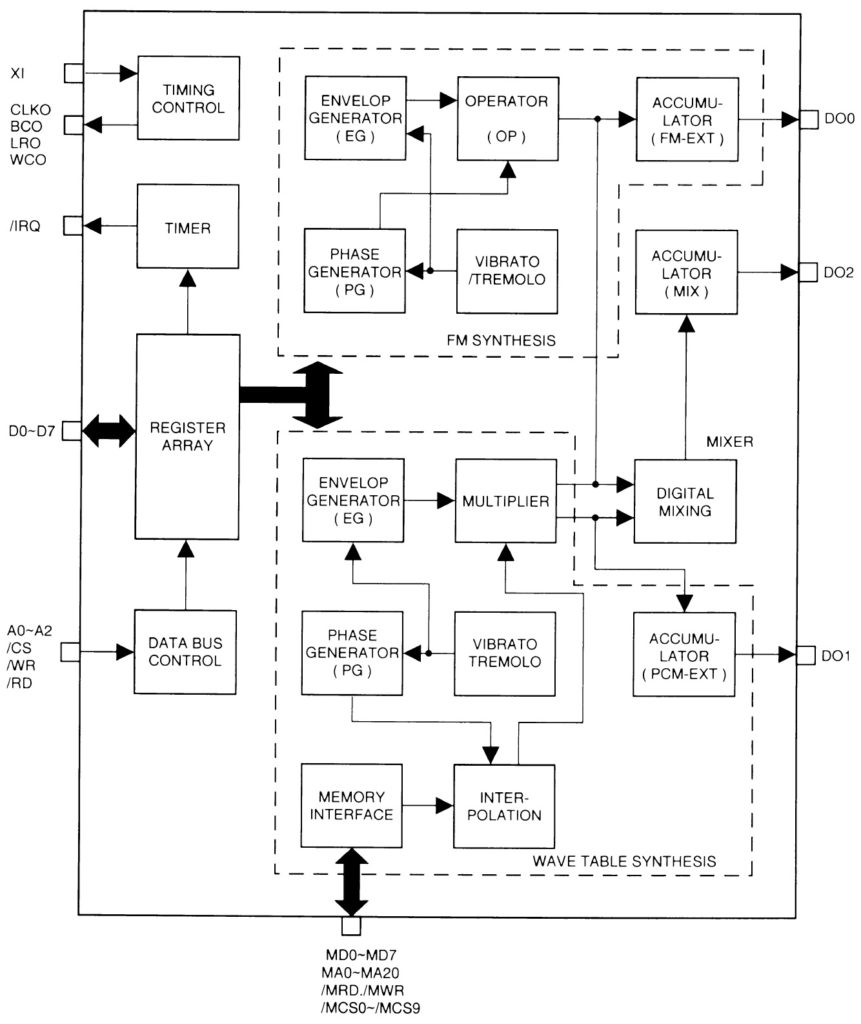
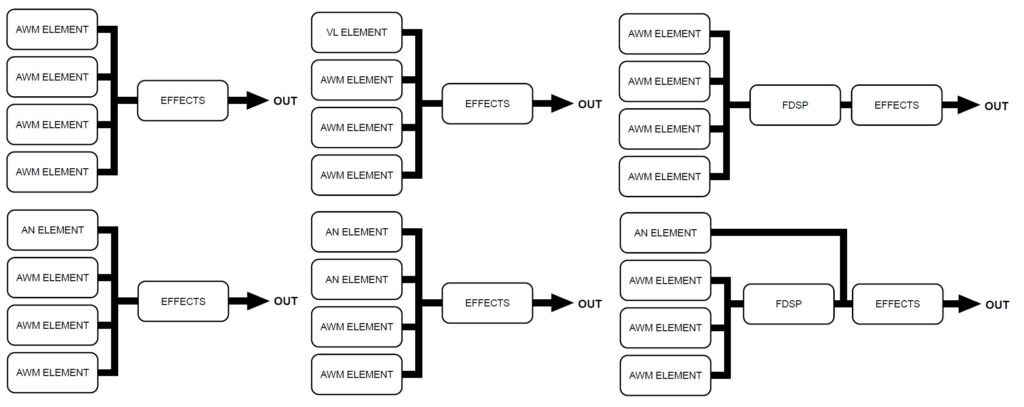
AWM, AN, VL and FDSP can be combined (layered) in a variety of ways. (See the EX5/EX7 manual for details.) All of the synthesis methods share a common element structure as shown in the image below.
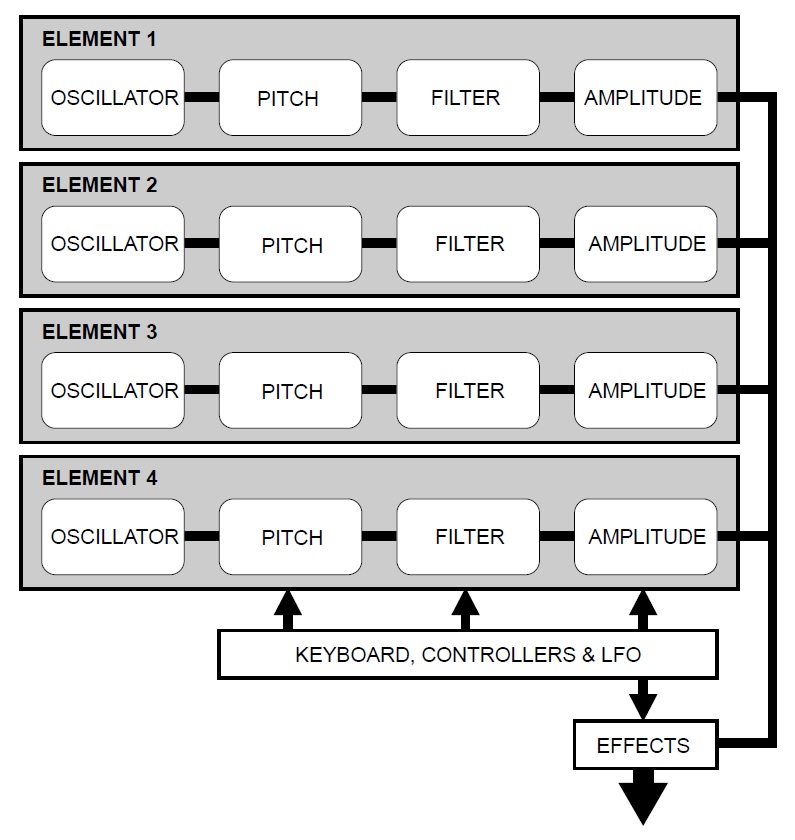
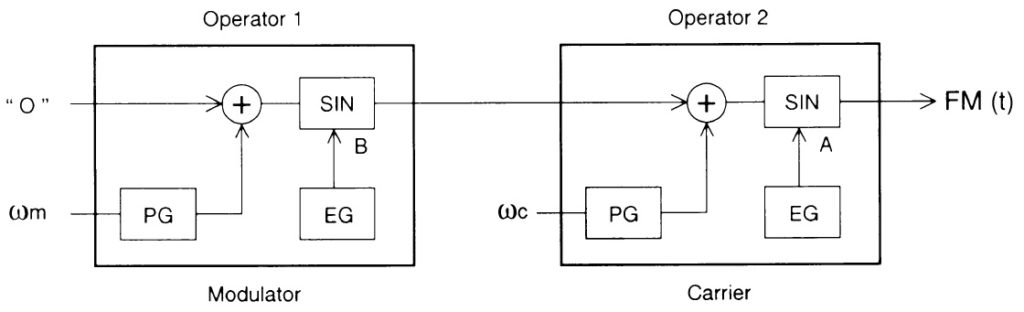
The main difference between the synthesis types is how the “oscillator” is handled:
- AWM: The oscillator is formed via sample-playback.
- VL: The oscillator is the instrument model (mouthpiece, bow/string, etc.)
- AN: The oscillator is a simulated VCO (Voltage Controller Oscillator).
- FDSP: Same as AWM.
The remainder of sound processing is based on the standard AWM pipeline with the addition of a few extra VL, AN and FDSP parameters.
All is exciting and fantastic until one reads the polyphony spec:
Voice Type EX5/5R Polyphony EX7 Polyphony
-------------- ---------------- -------------
AWM/Drum 126 64
VL+AWM 1+AWM
FDSP 16 8
AN(Poly)+AWM 2+AWM 1+AWM
AN(Layer)+AWM 1+AWM
AN+FDSP AN:1; FDSP:8
So, I would forget about that fat stack of AN or VL oscillators (layers). Forget phat two-handed analog chords.
How did Yamaha create this many-headed beast? Glancing at the EX5 service manual, the EX5 tone generation hardware consists of two SWP30B processors configured in the age-old master/slave tandem. (The SWP30B is two generations older than the current SWP70.) The EX7 has only one SWP30B. Further clues come from Yamaha itself:
The DSP (Digital Signal Processing) system used to create the EX effects is also used by the AN, FDSP, and VL (EX5/5R only) tone generators to create voices. This means that less DSP capacity is available to produce effects when the aforementioned voice types are used. This imposes limitations which are different for the EX5/5R and EX7. The Reverb and Chorus effect units function normally regardless of the type of voice used.
There are no limitations to using insertion effects in the EX5 or EX5R Voice mode. In the Performance mode, however, insertion effects can be used on a maximum of 4 parts (voices) if the performance setup consists entirely of AWM voices. If a VL, AN, or FDSP voice is used in the performance setup, however, an insertion effect can only be used on one part (voice).
Colloquially, Yamaha have robbed Peter to give to Paul.
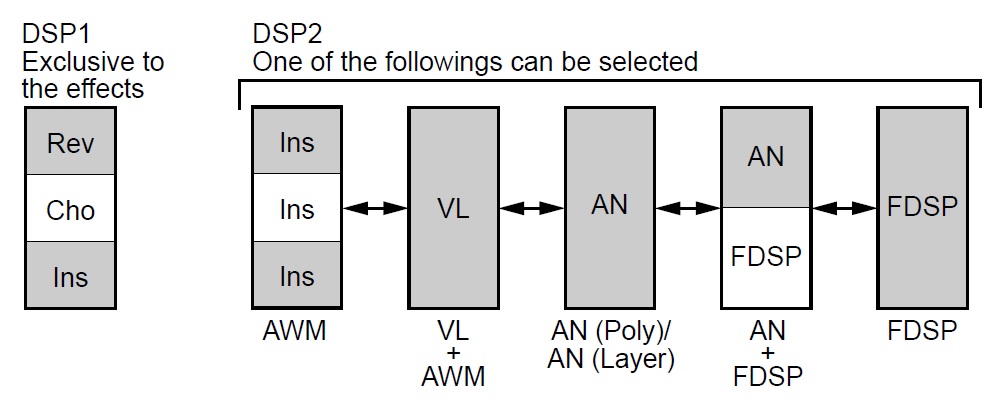
In EX5, DSP1 is always assigned to reverb, chorus and one level of insert effects. DSP2, however, is flexibly assigned between insert (AWM), VL, AN, and FDSP. Likely, Yamaha returns DSP2 output to a single TG channel in the front-end of the AWM2 pipeline (i.e., a return datapath).
Given the limitations in the EX5 internal architecture, I understand why Yamaha deployed the SSP2 digital signal processor in the Reface CS. Reface CS uses AN Analog Physical Modeling and is eight voice polyphonic. Although Yamaha don’t say much about its filter, Reface CS is not restricted as to filter algorithm (i.e., can be something other than the AWM2 hardware filters).
Sometimes you need to look back in order to see forward. AN-X™ is on the horizon and we will soon see if Yamaha raids its treasure vault. [Again, 25 years later.]
Copyright © 2023 Paul J. Drongowski