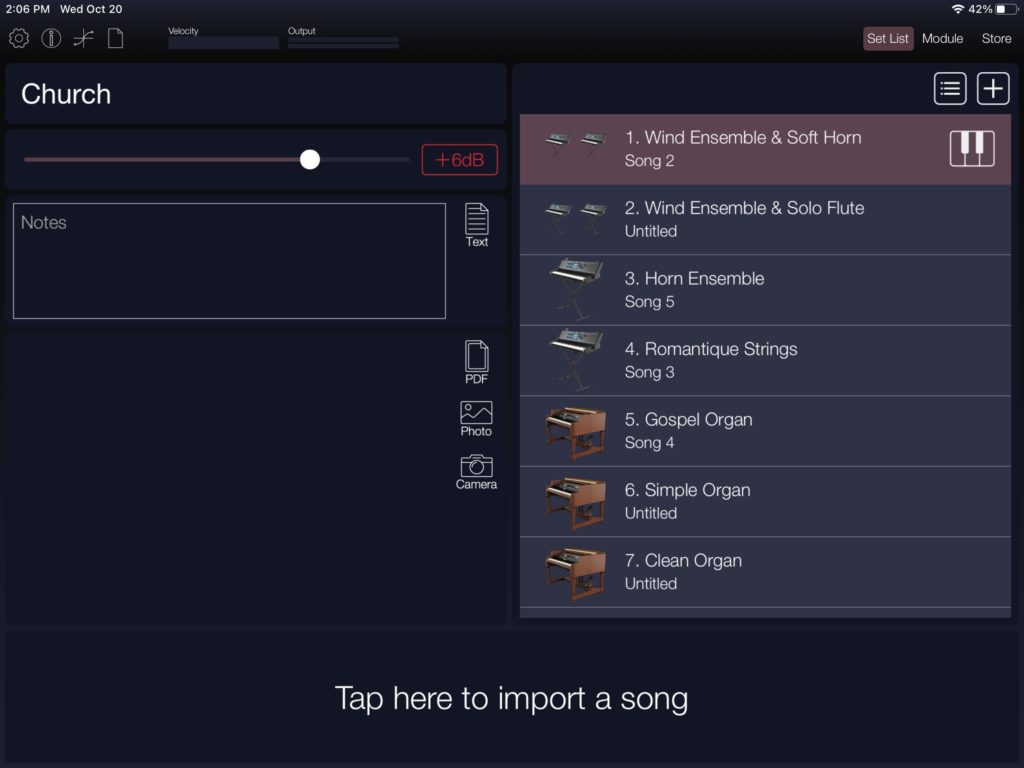
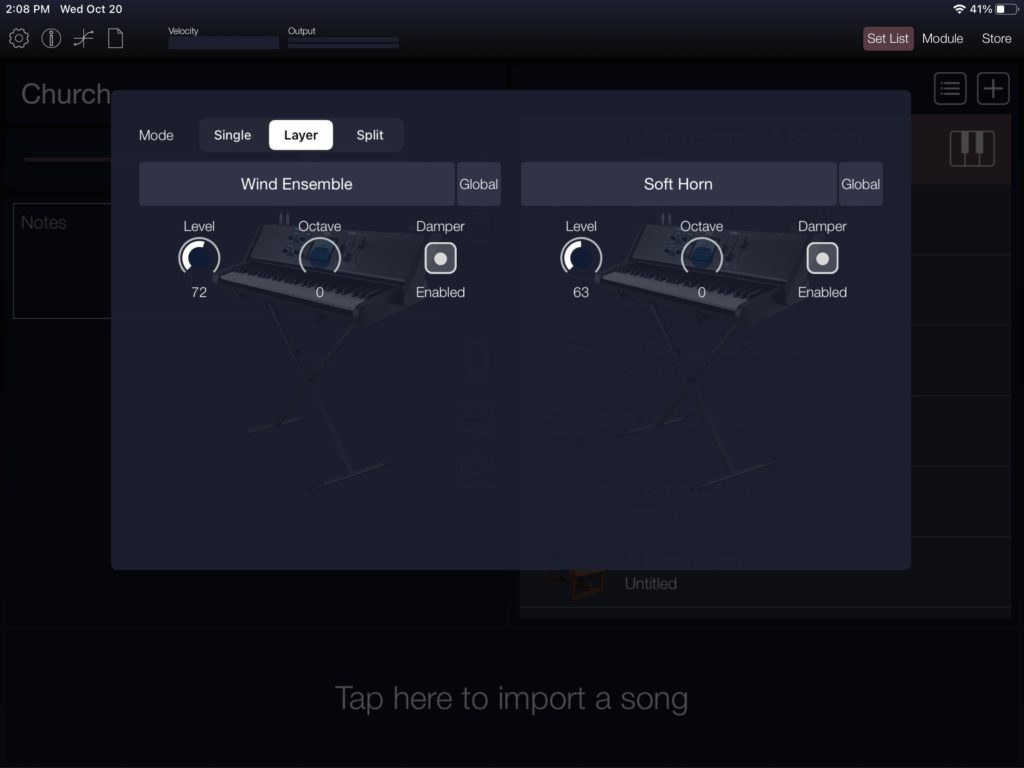
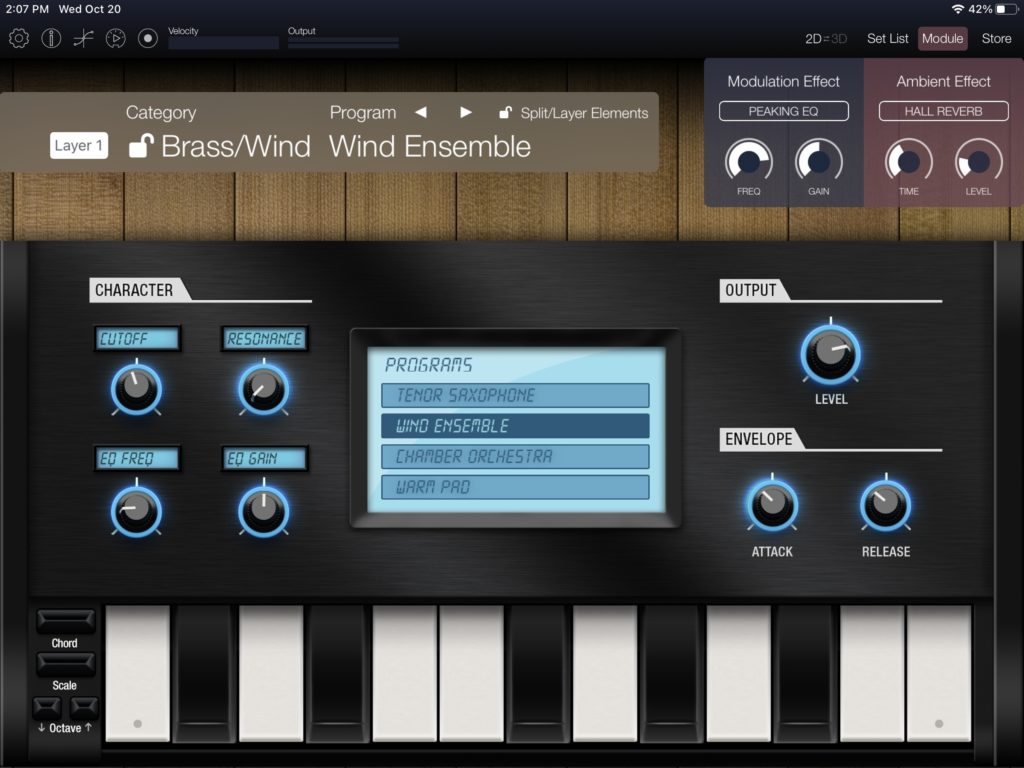
I like the Korg Module Pro “GospelOrgan” patch, so I tried to create a sound-alike voice on Yamaha Genos. Genos and MODX share the same waveforms and DSP effects, and I may port the result to MODX, too.
The experience recalled my previous misgivings about the rotary speaker simulation and limitations of the Genos DSP effect implementation. I will amplify those comments here.
Mid- to upper-level Yamaha arranger workstation have long had a drawbar organ feature which Yamaha calls “Organ Flutes.” This feature dates back to 1999, appearing in the PSR-9000 keyboard. Although a few details have changed over the years, Yamaha has not substantially overhauled Organ Flutes. It’s time, Yamaha — the world has moved on. I’d love to see the new YC organ technology in Genos. It’s the flagship of the arranger line and YC organs would definitely differentiate Genos from its lower-cost brethren.
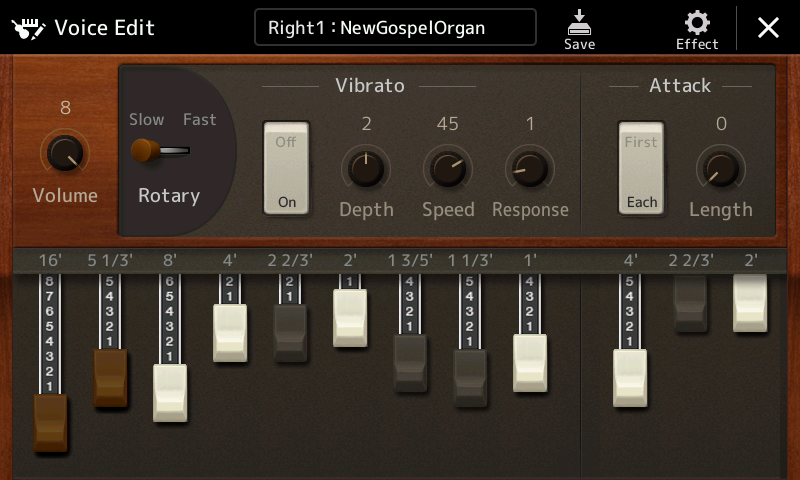
The main, tweakable organ parameters are:
- Nine drawbars
- Percussion (first note/each note, length)
- Percussion pitch (4′, 2-2/3′, 2′)
- Response (onset delay of drawbar and percussion sounds)
- Vibrato (on/off, depth, speed)
- Rotary speaker speed (slow/fast)
- Volume level (1 to 8)
- DSP effect (e.g., rotary speaker)
For B-3’ers, the 4′ percussion pitch is the 2nd harmonic setting and the 2-2/3′ percussion pitch is the 3rd harmonic setting. The 2′ pitch supports non-Hammond organs which require it.
Compared with a contemporary clonewheel, one immediately notes a few missing features:
- Vibrato only, no chorus
- No key click
- No rotor noise
- No leakage
Overall, the Genos B-3 is super clean and polite — not vintage. MODX (Montage) provides key click, rotor noise (grit) and rotor whistle waveforms. Why does Genos lag behind? Although MODX is AWM2, not modeling, these extra waveforms are better than nothing at all.
The Genos synthesis engine is also AWM2 sample-playback and AWM2 provides the Organ Flutes vibrato. Organ Flutes does not simulate the one-of-a-kind Hammond vibrato/chorus scanner. The Korg Module “Gospel Organ” voice incorporates C-3 chorus and the AMW2 vibrato just doesn’t cut it (head-to-head comparison). I had to substitute Genos’ V-2 setting and move on.
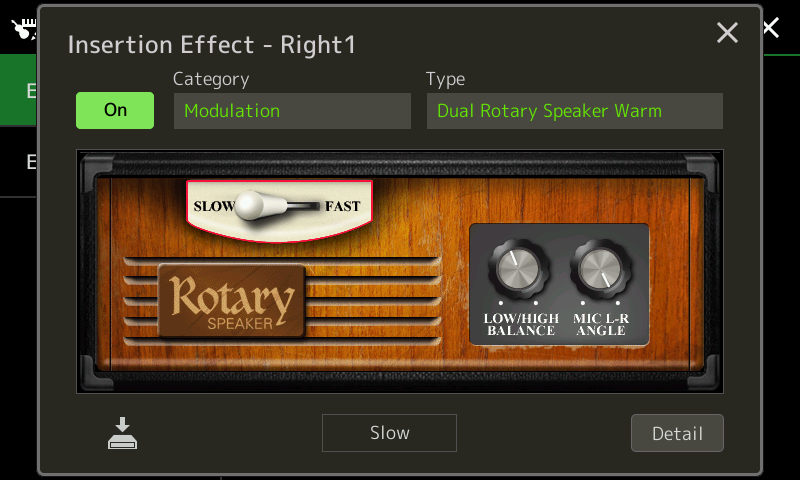
If you want to change the rotary speaker type, you need to dive through the effect setting button at the top of the Organ Flutes screen. After selecting the insertion effect, Genos displays a skeuomorphic (graphical) rotary speaker cabinet with a few knobs. In the screenshot above, we get rotary speed, horn and rotor balance, and microphone left/right angle. Like many (most?) rotary speaker simulations, the rotary effect emulates the sound of a mic’d up, stereo recording of a Leslie, not a horn and rotor moving air in a room.
Additional rotary speaker (DSP) parameters are changed by tapping the “Detail” button in the lower right corner. deep-diving reveals a few more deficiencies:
- Missing parameters due to a limitation on the number of DSP effect parameters (16 parameters maximum)
- Only one insert effect (typically the rotary speaker)
- Volume control is post-effect and does not affect overdrive
Here is a little more information about each issue.
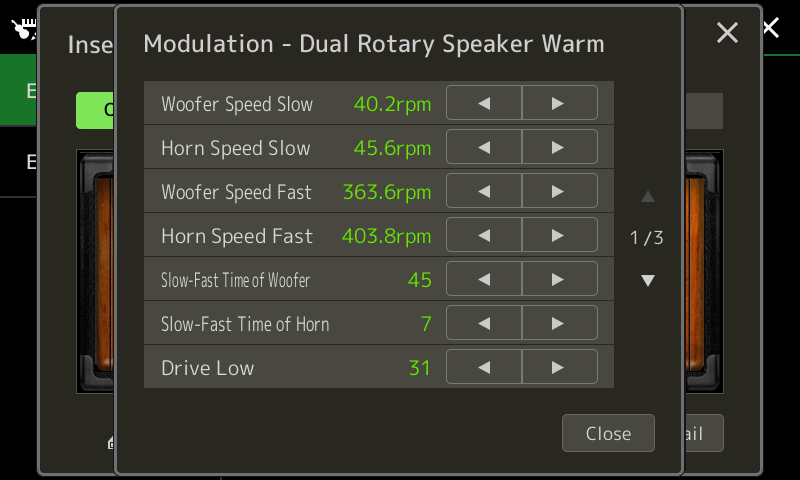
At heart, the Genos (PSR, Tyros) sound engine implements the Yamaha XG synthesis and effects architecture. The XG architecture allows up to sixteen (!6) parameters per DSP effect unit. Unfortunately, Yamaha’s DSP engineers are creating effect algorithms (AKA “effect types”) with more than sixteen parameters! The MODX ROTARY SPEAKER 2 algorithm has eighteen (18) parameters. The Genos REAL ROTARY effect type is the same algorithm as MODX. However, only 16 parameters are accessible or stored on Genos. The two missing REAL ROTARY parameters are:
- Slow-Fast Time of Rotor
- Fast-Slow Time of Rotor
You cannot change these rotor ramp times on Genos, yet, you can change them on MODX.
This issues affects the Genos UNI COMP compressor algorithm (MODX: UNIVERSAL COMPRESSOR DOWN). Dare I mention the inability to specify a side-chain part, too? People are trying to create EDM on arrangers.
The XG architecture allows only one insert effect per part. The Organ Flutes insertion effect is typically a rotary speaker simulator. The MODX effect architecture, on the other hand, allows two insert effects per part. Yamaha synths take advantage of the second insert effect to add overdrive or vintage EQ:
- Rotary speaker 1 → Multi FX (Distortion Solo)
- Rotary speaker 2 → VCM 501 EQ (Flat)
- Amp Simulator 3 (Tube) → VCM 501 (Flat)
- Amp Simulator 1 (Stack 2) → Rotary Speaker 1
- VCM 501 EQ (Flat) → Rotary Speaker 1
The rotary speaker drive alone is not enough to warm up the basic sound nor is it enough to get a sweet, realistic overdrive with guts. I experimented with the Genos REAL ROTARY effect and got some very squirelly results at high drive levels. The algorithm can be pushed in unexpected, undesirable ways while searching for true funk.
Unlike a real Hammond/Leslie combination, the Genos expression pedal controls post-effect part volume. This is like putting the volume control after the Leslie speaker. A Hammond B-3 pedal controls the level into the Leslie pre-amp. Thus, the pre-amp frequency characteristics and overdrive track the Hammond pedal. The Yamaha YC61 modeling gets this right. Putting the volume pedal before the pre-amp lets the player get clean or dirty in the same way a guitarist uses picking and/or the guitar volume knob to distort or clean up their tone.
If the Genos developers must work around the XG architecture, they should consider a new effect algorithm that combines overdrive with the rotary speaker simulation. The algorithm should allow foot pedal control over the Leslie pre-amp input level. Genos and other PSRs allow wah pedal control, so they obviously know how to achieve this capability within the current architecture.
Copyright © 2021 Paul J. Drongowski