I want to give a shout out to Lionel on the PSR Tutorial Forum. He posted a very nice PSS-A50 mod — stereo!
Yep, the PSS-A50 is stereo and, as Lionel discovered, the in-built samples are also stereo. Check out Lionel’s PSS-A50 stereo mod video. His video begins with a great close-up of his changes to the PSS-A50 digital main board (DM).
As noted in my PSS-A50 look inside, the central computer and tone generator is Yamaha’s SWLL processor (YMW830-V). The SWLL is a system-on-a-chip (SOC) which integrates the host CPU, working memory, key/display scanner, and tone generator. Just add a 37-key keyboard, display driver, 2MByte serial flash program/waveform ROM, USB controller, audio electronics and power electronics, and you have a complete ultra-low cost synthesizer.
The digital-to-audio converters (DAC) are integrated into the SWLL. The SWLL has six DAC-related pins:
- DACLPP (pin 1)
- DACLMM (pin 2)
- DAC_VDD (pin 3)
- DAC_VSS (pin 4)
- DACRMM (pin 5)
- DACRPP (pin 6)
DAC_VDD and DAC_VSS are conversion reference voltages. DAC_VDD is derived from DAC_VCC produced by a low drop-out voltage regulator (Texas Instruments TLV74333PDBVR). DAC_VSS is ground.
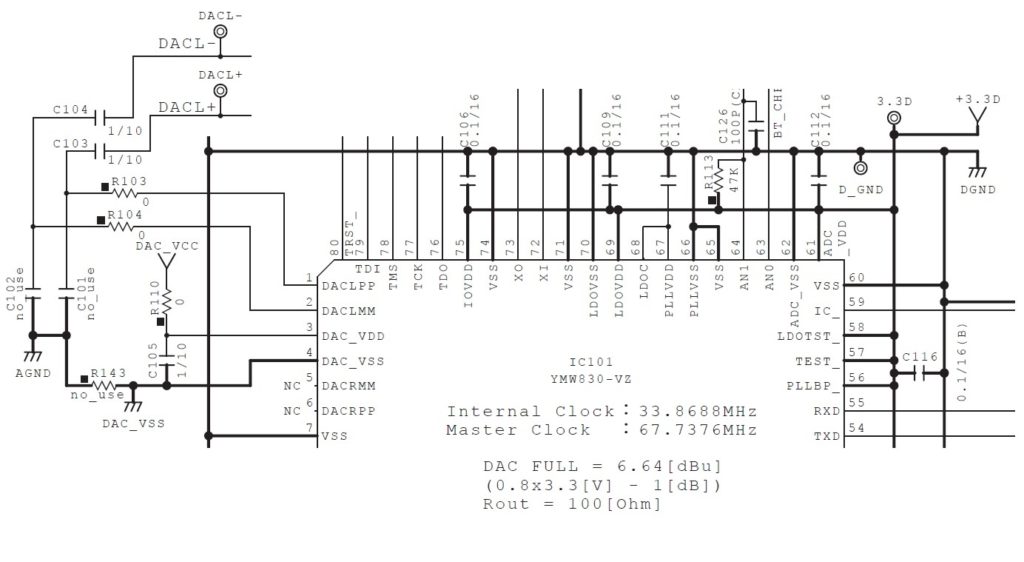
DACLPP and DACLMM are differential audio signals for the left channel. DACRPP and DACRMM are differential audio signals for the right channel. DACRPP and DACRMM are left unconnected in the PSS-A50. There are two test points, DACL- and DACL+, on the printed circuit board (PCB), in case you would like to probe these signals.
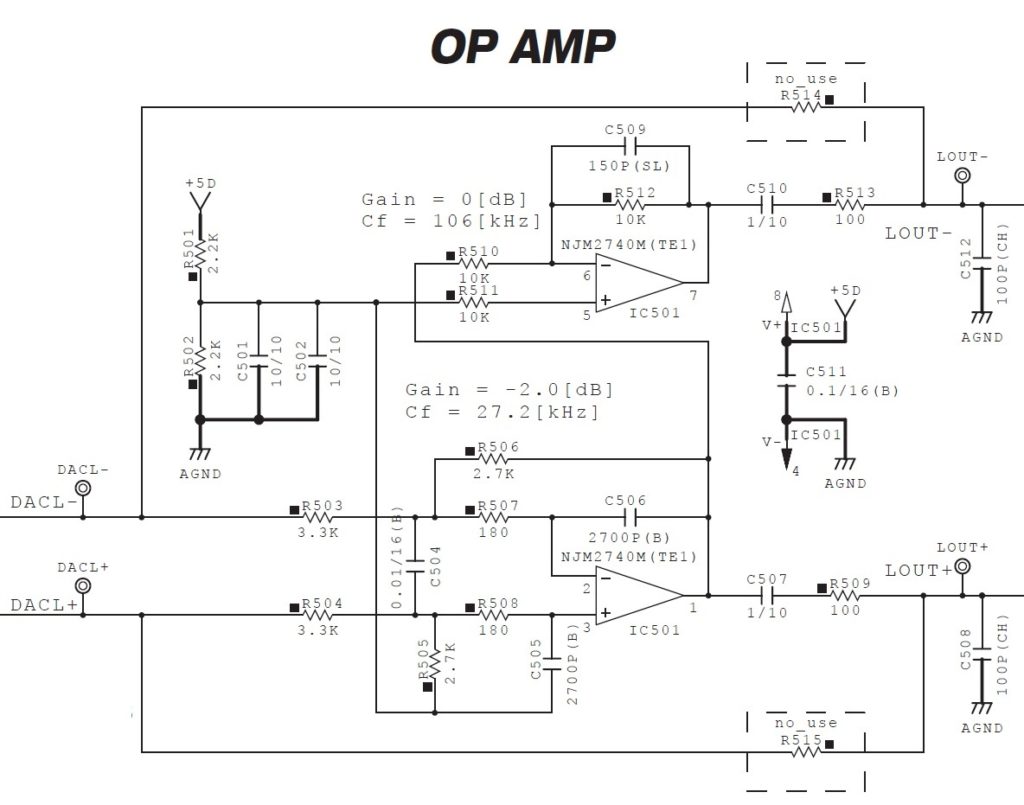
DACL+ and DACL- feed two operational amplifiers which are low pass filters. The low pass filters produce signals LOUT+ and LOUT-, which are sent to the plus and minus inputs of the headphone amplifier (TPA6132A2RTER) and speaker power amplifier (Rohm BD27400GUL). It’s differential audio signals all the way, presumably, to keep noise low.
The Texas Instruments TPA6132A2RTER is a 25 mW stereo headphone amplifier. The Rohm BD27400GUL is a low voltage class-D monaural speaker amplifier.
I have to admire Lionel’s construction skills as it is quite difficult to solder wires to a surface mount IC. Nice work replicating the stereo low pass filters, too.
Keep the Yamaha PSS-A50 hacks coming! Please don’t forget the PSS-A50 MIDI mod.
Here are some additional Yamaha PSS-related stories:
- Review: Yamaha PSS-A50
- Yamaha PSS-A50 MIDI notes
- Yamaha PSS-A50 MIDI limitations
- Yamaha PSS-A50 motion effects
- PSS-A50: Power to the people
- Review: Yamaha PSS-E30 Remie
- Inside Yamaha PSS-E30 Remie
- Ye olde Yamaha Dance kit
Copyright © 2022 Paul J. Drongowski