Thanks to Dmitry Ko on the Keyboard Corner forum, we have the first solid information about Montage M7 internals! Congratulations, Dmitry!
We owe Dmitry a round of applause and gratitude for providing the first — and extensive — information about Montage M internals. He had to take extra steps to find and identify some components (more than I would have been willing to do with a brand new board, that’s for sure).
Dmitry was kind enough to give me a preview and his analysis is spot on.
Here are my own notes:
IC601 SWP70 #1 (Upper left DM PCB) YMW832-C FM-X? IC602 Winbond W9812G6KH-5 SDRAM 128 Mbit Parallel 200MHz (8M x 16) IC401 SWP70 #2 (Middle) YMW832-C IC501 Winbond W9812G6KH-5 SDRAM 128 Mbit Parallel 200MHz (8M x 16) IC402 Winbond W9825G6KH-6 SDRAM 256 Mbit Parallel 166MHz (16M x 16) IC403 Winbond W29N08GVSIAA NAND flash 8 Gbit (1G x 8) IC404 Winbond W29N08GVSIAA NAND flash 8 Gbit (1G x 8) IC405 Winbond W29N08GVSIAA NAND flash 8 Gbit (1G x 8) DM PCB rear IC406 Winbond W29N08GVSIAA NAND flash 8 Gbit (1G x 8) DM PCB rear IC201 SWP70 #3 (Right) YMW832-C IC301 Winbond W9812G6KH-5 SDRAM 128 Mbit Parallel 200MHz (8M x 16) IC202 Winbond W9825G6KH-6 SDRAM 256 Mbit Parallel 166MHz (16M x 16) *IC205 Winbond W29N08GVSIAA NAND flash 8 Gbit (1G x 8) *IC206 Winbond W29N08GVSIAA NAND flash 8 Gbit (1G x 8) *IC207 Winbond W29N08GVSIAA NAND flash 8 Gbit (1G x 8) DM PCB rear *IC208 Winbond W29N08GVSIAA NAND flash 8 Gbit (1G x 8) DM PCB rear XL201 02238 SWP70 clock IC701 SSP3 YJ496A0 XL701 SSP3 clock IC706 TI LV08A 2BK ATPZ XL801 SSP3 clock XLB02 USB hub clock ICB04 GL852G Genesys Logic 4-port hub USB 2.0 (SSP3 hub) Q1102 TPC812S ??? USB2_VBUS IC702 SDRAM No mount? ICA01 Texas Instruments Sitara AM5728BABCXA IC001 NANYA 2245 NT5CC128M16JR-EK DDR3 256MByte IC002 NANYA 2245 NT5CC128M16JR-EK DDR3 256MByte XLE01 CPU clock ICB03 GL852G USB 2.0 hub controller (DM PCB rear, CPU hub) XLB01 USB hub clock ICC02 eMMC (Yamaha YN240B0) ICC01 Fast Ethernet PHY ICA03 THine THC63LVD1O3D LCD controller (LVDS) IC904 Texas Instruments TPS659037 Power controller IC101 Texas Instruments PCM1795 32-bit stereo DAC DM PCB rear IC111 Texas Instruments PCM1795 32-bit stereo DAC DM PCB rear IC121 Texas Instruments PCM1804 24-bit stereo ADC DM PCB rear
In a few cases (marked with “*”), copyright labels obscure the chip ID information on the IC package.
Here are a few additional observations.
Yamaha gave the Montage M a major league host CPU: Texas Instruments Sitara AM5728BABCXA. The Sitara is multi-core:
- Dual-core ARM Cortex-A15 MPU (1.5 GHz)
- Dual TMS320C66x floating-point VLIW DSP (750 MHz)
- 2 x dual-core ARM Cortex-M4 co-processors (213 MHz)
- Dual-core PowerVR SGX544 GPU (532 MHz)
This is a major step up from the single core 800MHz ARM in the original Montage. The Sitara is given twice as much primary memory than the original: 512MBytes of DDR3 RAM.
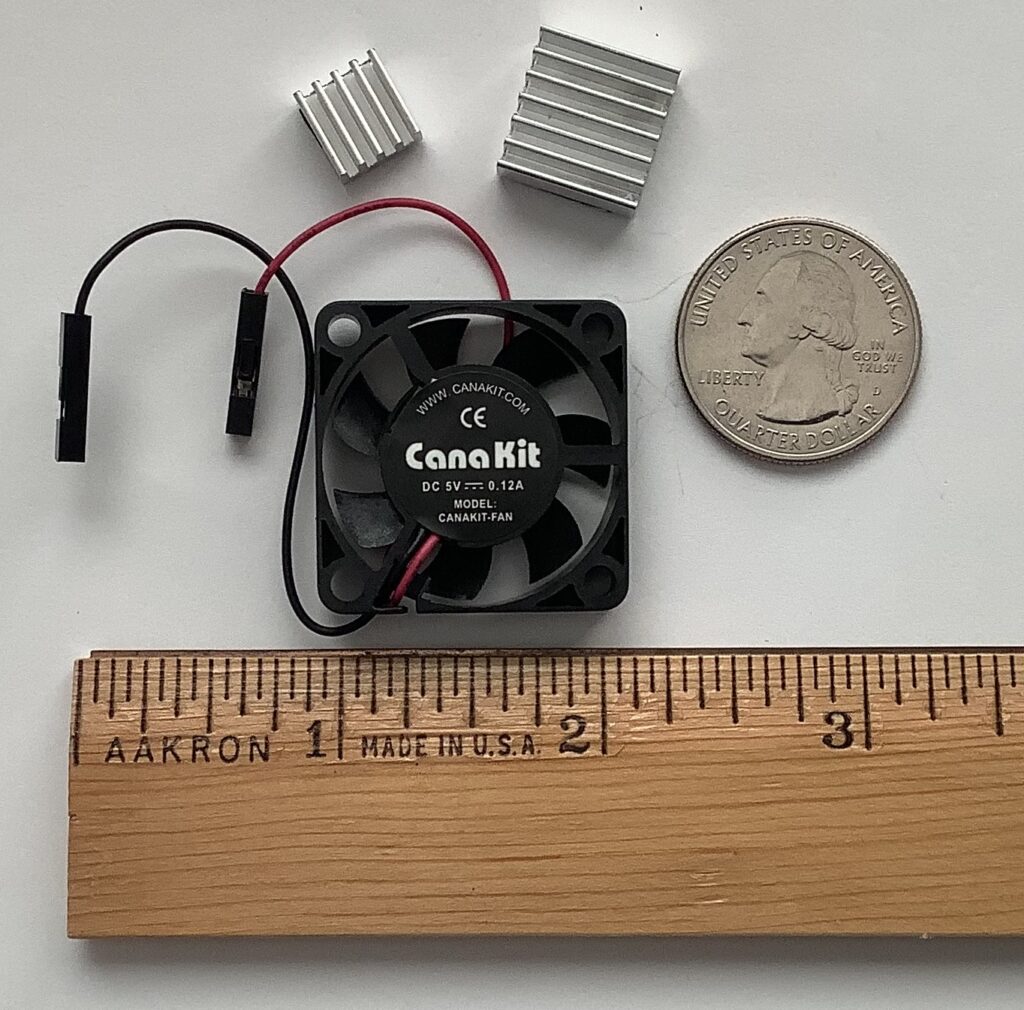
Thus, folks, you’re going to need a fan. Montage M’s digital logic board (DM) has a substantial metal cover, probably to control RFI. The Sitara has a vanilla heat sink. An opening in the metal cover lets heat escape from the heat sink. The fan draws air from beneath the metal cover/heat sink. This design is different than what I expected, i.e., a very small heat sink plus mini-fan cooler a la Raspberry Pi. This Sitara ain’t no RPi!
The two integrated TMS320C66X DSP cores likely synthesize AN-X. 16 voice AN-X polyphony feels just about right for two TMS320 cores. (Reface CS employs an SSP2 DSP and has 8 voice polyphony.) With compute-intensive AN-X going on, you’re gonna need a fan. I don’t buy the cooling pipe solutions proposed by some and it would be very difficult to position the Sitara in contact with the metal chassis. End of story.
The factory waveform NAND flash is Winbond W29N08GVSIAA. That is the highest capacity ONFI compatible NAND flash made by Winbond. The factory waveforms are compressed (10GB when converted to 16-bit linear format) and reside in 4GBytes of physical NAND flash. User waveforms are uncompressed (3.7GB available capacity) and reside in 4GBytes of (separate) physical NAND flash.
In the original Montage, factory and user waveforms are co-resident in 4GBytes of waveform NAND flash. Yamaha added a third SWP70 tone generator/effects IC and, as we know, dedicated one SWP70 to factory waveforms and another SWP70 to user waveforms. The third SWP70 doesn’t have waveform memory and synthesizes FM-X.
A label covers the top of the eMMC device which provides bulk storage (OS, software, presets, etc.) for the Montage M. The original Montage has a 4GByte eMMC device.
As expected, the SSP2 is out of production and is replaced by SSP3. The SSP3 inherits the digital audio routing and rate conversion chores performed by the original’s SSP2. The SSP3 has its own integrated USB interface and associated USB2.0 4-port hub. All are co-located with the external USB connector.
The THine LVDS handles LCD display duties. The Sitara has serious graphics chops with its dual PowerVR SGX544 GPUs. I haven’t worked out the interface to Montage M’s OLED subdisplay as yet. Genos1 communicates with its subdisplay via SPI.
Thanks, again, Dmitry! This more than enough for the next round of Internet speculations. 🙂
Copyright © 2024 Paul J. Drongowski